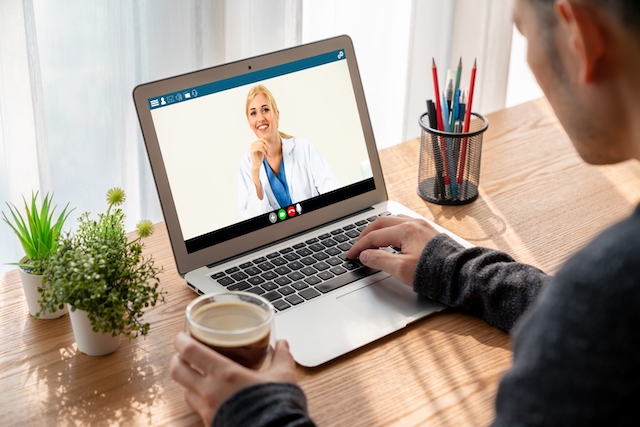
Digital health platform reduces hospital stay for surgery patients
A recent study has highlighted the significant benefits of a digital health platform named Pip Care in enhancing the postoperative recovery process for patients undergoing surgery. The research, published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, demonstrates the platform’s ability to reduce hospital stays through effective engagement with patients and integration of personalised recovery strategies.
Pip Care is designed to support patients throughout their perioperative journey by offering personalised care plans and connecting them with certified health coaches. These coaches collaborate with the patients’ surgical teams to provide tailored guidance and daily recovery tasks. The platform’s objective is to foster patient adherence to recovery plans, thus improving surgical outcomes.
The study was conducted in collaboration between UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine. Researchers invited patients scheduled for elective surgeries at an academic medical centre over a period from November 22, 2022, to March 27, 2023, to participate in the platform from approximately two to four weeks pre-surgery to four weeks post-surgery. Out of 283 patients approached, 172 (60.8%) enrolled in the study. A notable 83.1% of these participants engaged in one or more health coaching sessions, with 97.2% proceeding to surgery, surpassing the industry’s typical 90% to 93% surgical adherence rates. Post-surgery, 70.3% continued to engage with the platform.
The platform maintained an impressive 82% weekly engagement rate, with patients frequently attending multiple health coaching sessions. Feedback gathered from 95 survey submissions revealed high levels of satisfaction, with many patients affirming that the coaching significantly aided their perioperative experience.
A comparative analysis between 128 patients using the Pip Care platform and 268 non-users undergoing the same procedures at the same hospital showed that platform users experienced a 24% reduction in postoperative hospital stay. Specifically, the average stay for Pip Care users was 2.4 days compared to 3.1 days for those not using the service. However, both groups recorded similar rates of return to emergency departments within 30 days post-operation.
Dr. Aman Mahajan, MD, PhD, Peter and Eva Safar Professor and Chair of the Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, emphasised the challenge of ensuring adherence to perioperative care plans. He noted, “Ensuring that patients follow through with their prescribed perioperative care plans is crucial for their health and recovery outcomes, but achieving this adherence is often challenging.” Dr. Mahajan hailed the integration of this hybrid digital-telemedicine platform as a significant advancement in clinical care, offering ease of use for both patients and clinicians while enhancing patient outcomes and satisfaction with surgical procedures.
This study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting digital healthcare’s role in improving the continuity of care in surgery. For instance, a 2022 study from the University of Alabama Birmingham indicated that telehealth interventions had substantially reduced no-show rates among surgical patients. The American College of Surgeons has endorsed telehealth, recognising its potential to enhance access to surgical care, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas, and to empower patients in their health care journeys by facilitating active participation in virtual consultations.
Read More
California healthcare giant drives digital health forward with innovative AI centre in San Francisco
Nestled within a spacious and modern environment, boasting stunning vistas of the Bay Bridge, a dynamic team that could easily be mistaken for a tech startup’s brightest is on the brink of revolutionising health care delivery. Sutter Health has inaugurated an “innovation centre” at the iconic Pier 1 in San Francisco, situated just a few strides from the bustling Ferry Building. This centre is the crucible where the future of healthcare, infused with the latest in mobile technology and artificial intelligence (AI), is being forged.
As the most expansive health system in Northern California, Sacramento-headquartered Sutter has embarked on this venture with a seven-year lease of an 11,000-square-foot office space, opened for its employees just this month. This initiative is not merely an expansion but a declaration of Sutter’s commitment to San Francisco and, more importantly, to AI as an indispensable component of future health care paradigms. This commitment comes at a critical juncture, contrasting sharply with the trend of businesses scaling down or exiting the city.
Sutter Health is no stranger to San Francisco, operating two significant hospitals within the city’s bounds – CPMC Van Ness and CPMC Mission Bernal. Although it previously maintained non-clinical office spaces in the city, the pandemic prompted a shift towards remote work, leading to the closure of its Battery Street office. The newly launched innovation centre, however, marks the first dedicated space for Sutter’s engineers, developers, and designers to collaborate closely with tech firms on digital health applications and remote monitoring systems aimed at integrating health care seamlessly into the fabric of daily life.
Chris Waugh, Sutter’s chief innovation officer, highlights the strategic importance of this centre as a significant leap forward. It will not only serve as a showcase for technologies developed in-house, such as the Scout mobile app for monitoring adolescent mental health and the Continuous Care Program for home-based blood pressure management for hypertension patients, but it will also feature futuristic concepts like a prototype “hospital room of the future”. This room will be equipped with devices that not only automate the updating of medical records but also offer a space where patients can receive assistance with digital health applications, reminiscent of a Genius Bar setup like in Apple stores.
The centre’s role extends beyond the confines of physical health examinations. It is envisaged as a virtual health care hub, where Sutter’s health coaches will provide tele-health services, from consultations to health management advice, through digital screens.
Moreover, Sutter is advancing the development of digital tools designed for home use. These include sensors for beds, refrigerators, and stoves that can detect changes in daily movement patterns, potentially alerting to health risks such as falls – a significant concern for the elderly population.
In a bid to further entrench itself in the digital health landscape, Sutter is cultivating partnerships with tech firms specialising in AI and other digital health innovations. One such partnership is with Ferrum, a Sunnyvale-based tech company that offers a secure platform for accessing a suite of AI tools, including an AI-assisted program for early lung cancer detection.
Pelu Tran, CEO and co-founder of Ferrum, envisions the innovation centre as a nexus for collaborative efforts with Sutter’s clinical leaders, fostering a more proactive and extensive engagement with the Bay Area’s AI ecosystem.
The decision to locate the innovation centre at Pier 1 was influenced by its accessibility for employees commuting from various parts of the Bay Area, according to Waugh. He expresses a bullish outlook on San Francisco’s future, positioning Sutter’s investment as a pledge to the city’s resurgence. “We’re optimistic and betting on the city,” he asserts, inviting others to join in shaping San Francisco’s revival narrative.
Through this pioneering innovation centre, Sutter Health is not just betting on AI and digital technology as the future of healthcare; it is actively shaping that future, making a profound investment in the health and wellbeing of the San Francisco community and beyond.
Read More
Digital health solutions must adapt to elderly needs, South Korean study shows
A recent investigative endeavour originating from South Korea sheds light on the nuanced relationship between the elderly population and their engagement with digital healthcare solutions. This intricate study, a collaborative effort spearheaded by esteemed institutions and corporations such as Seoul National University, Yonsei University, aged care specialist Silvia Health, and digital therapeutics pioneer WELT Corp., embarks on an exploration to dissect the utilisation patterns and satisfaction levels derived from healthcare applications and wearable health devices among older Koreans.
The research team embarked on a pioneering journey to delineate the disparities in digital health technology adoption between seniors who are either pre-frail, frail, or healthy. This distinctive approach has positioned them as frontrunners in analysing how frailty influences digital health technology use within this demographic.
Garnering support through a grant from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, the findings of this pivotal study have been meticulously documented in the esteemed Journal of Korean Medical Science.
Engaging with a cohort of 505 participants, all aged 65 and above, the study reveals that 30% of these individuals are categorised as frail by Korean healthcare standards, with the remainder classified as healthy. A noteworthy revelation from this survey is the digital literacy gap among the respondents: whilst all participants are smartphone users, a significant 63% admit to facing challenges in managing mobile applications independently.
The investigation unveils that merely a quarter of the surveyed group actively utilises healthcare applications, with a higher propensity observed among the healthy elderly. For the frail segment, these digital tools serve primarily as conduits for accessing healthcare information and procuring medical advice, significantly enhancing their self-care capabilities and the management of personal health data.
Conversely, the adoption of wearable health devices remains markedly low, with just 36 out of the 500+ respondents integrating such technologies into their daily lives. These devices, ranging from smartwatches to patch-type gadgets, are predominantly utilised for monitoring physical activity. It emerges that healthy individuals appreciate the convenience offered by wearable devices more than their frail counterparts, who, however, value these devices for their potential to aid in making critical healthcare decisions, such as the timing of hospital visits.
South Korea stands at the cusp of a demographic shift, with senior citizens currently constituting nearly 20% of its population, a figure anticipated to escalate sharply in the coming decades. This evolving demographic landscape underscores the urgency for tailored digital health solutions that cater specifically to the elderly’s unique needs.
The study’s findings highlight a discernible disparity in the use of digital health tools between frail and healthy seniors, advocating for the development of technologies that are not only accessible but also specifically designed to address the distinct requirements of this age group.
The researchers articulate a compelling argument for a more nuanced approach to digital health technology, stressing the importance of understanding the elderly’s specific needs and expectations. They advocate for the integration of customised services into digital devices, particularly those that cater to the frequently used services by pre-frail and frail older adults.
In a country renowned for its high smartphone penetration rates, South Korea is uniquely positioned to leverage mobile health technologies to enhance the health outcomes of its ageing population. A previous study in 2022 highlighted the potential of these technologies to mitigate the impact of social determinants on health, emphasising, however, that they cannot supplant the traditional care settings.
This groundbreaking study not only illuminates the current landscape of digital health technology usage among the elderly in South Korea but also charts a path forward for the development of more inclusive and effective digital health solutions, ensuring that the ageing population remains connected, informed, and empowered in managing their health.
Read More
The delicate balance of preserving muscle mass in the age of weight loss pharmaceuticals
As the global population turns increasingly towards medications like Ozempic for weight loss solutions, a growing concern has emerged regarding the side effect of muscle loss associated with these treatments. This phenomenon has sparked a multifaceted response from various sectors aiming to mitigate this undesired outcome, thereby enhancing the overall health benefits of weight management efforts.
Luxury fitness centres are now tailoring strength-training regimes specifically for individuals utilising these medications, with the promise of maximising health results. These programmes are designed not just to counteract muscle degradation but to optimise the physical wellness journey of their clients. Concurrently, nutritional experts and bespoke meal delivery services are stepping up to formulate high-protein diet plans that support muscle maintenance amidst weight loss.
Pharmaceutical giants, including Eli Lilly, are at the forefront of innovation, developing drugs that offer a dual approach to weight loss by facilitating fat reduction while safeguarding or even augmenting muscle mass. Eli Lilly’s collaboration with BioAge Labs on the experimental compound azelaprag exemplifies this cutting-edge research. Azelaprag seeks to mimic the effects of exercise-induced hormones that play a critical role in muscle metabolism, offering hope for a more balanced fat-to-muscle loss ratio in patients taking drugs like Mounjaro and Zepbound.
Further expanding its arsenal, Eli Lilly’s acquisition of Versanis Bio introduces a novel approach to muscle preservation through bimagrumab, a drug that targets receptors involved in muscle and fat regulation. This promising development is backed by research suggesting enhanced muscle growth upon receptor blockade.
Clinical trials are also exploring combinations of existing weight loss drugs with new treatments to address the muscle loss conundrum. One such study involves the pairing of bimagrumab with semaglutide, the active ingredient in Ozempic, to investigate its potential in mitigating frailty in adults with obesity. Additionally, the FDA’s recent approval of a trial for a compound aimed at older adults signifies a proactive approach to preventing muscle deterioration alongside fat loss in this vulnerable demographic.
Despite the promise of these emerging treatments, their availability to the general public is anticipated to be several years away. This delay underscores the importance of immediate, accessible strategies for muscle preservation. Experts highlight the critical nature of maintaining muscle integrity, especially for older adults and postmenopausal women, who face a higher risk of frailty and osteoporosis with muscle loss. The consensus among healthcare providers is that a combination of protein-rich diets and strength training exercises remains a fundamental remedy against muscle depletion.
Capitalising on this need, companies are introducing products and services tailored to individuals on weight loss medications. From protein shakes designed to complement these drugs to specialised fitness programmes and nutritional counselling aimed at enhancing protein intake and mitigating malnutrition risks, the market is rapidly adapting.
Innovative telehealth solutions like Noom’s Muscle Defense programme, which integrates fitness guidance with dietary tracking, and fitness platforms such as Obé Fitness’s MuscleGuard, exemplify the digital response to this challenge. Additionally, initiatives like LifeTime Fitness’s clinic pilot in Minnesota, which combines personalised training with access to compounded weight loss medications, signal a growing trend towards holistic health solutions that encompass both pharmaceutical and lifestyle interventions.
While specialised programmes offer valuable support for muscle preservation, the essence of combating muscle loss lies in fundamental lifestyle adjustments. Incorporating moderate strength training and a balanced, protein-rich diet into one’s routine can be a pragmatic and effective strategy for those navigating the complexities of weight loss medications.
Read More
Digital health tools surge in popularity among Londoners
A groundbreaking report produced by the Health Innovation Network (HIN) South London and the NHS England (London) Digital First team reveals a significant shift towards digital healthcare engagement amongst London residents. The report, incorporating insights from over 3,000 London patients through online surveys and focus groups, discloses that nearly three-quarters of participants have embraced digital platforms like online consultation forms, the NHS App, and GP surgery websites for accessing primary healthcare services.
The report underscores the widespread appreciation for digital tools, citing their role in facilitating a more independent approach to healthcare management. The majority of respondents find these digital avenues not only user-friendly but also time-efficient, allowing for straightforward completion of essential healthcare tasks.
Despite the general ease of use, the report acknowledges disparities within London. Notably, 43% of respondents are unable to schedule routine GP appointments online, and nearly one-third lack comprehensive access to their medical records via the NHS App. Such variations highlight ongoing challenges in accessibility and feature availability.
The necessity to address digital exclusion is a critical component of the report, recognising the potential underrepresentation of digitally marginalised groups in such research. Efforts to combat the root causes of digital exclusion are emphasised as a priority.
The NHS App emerges as the most utilised digital tool, with 87% of survey participants reporting its use. The app is highly regarded for its informational value and the autonomy it provides in managing health, notably through medication reordering and health record access.
Online consultation forms are another key digital touchpoint, utilised by 77% of respondents. These forms are praised for reducing travel and waiting times, although challenges such as limited availability and the complexity of the forms are noted concerns.
GP surgery websites have been accessed by 76% of those surveyed, with users finding them beneficial for directing towards self-care and detailing GP service access. While improvements in website quality are noted, issues with navigation, appointment booking, and outdated information persist.
The report proposes several recommendations, including enhancing patient communication about available digital tools, pursuing higher standards in usability and accessibility, and adopting a patient-centred approach in service design and delivery.
Feedback from patients suggests that GP practices should extend the availability of online forms and increase the number of appointments bookable online. Additional suggestions include implementing mechanisms for timely patient feedback and ensuring all repeat medications in the NHS App are orderable. The report also addresses digital exclusion, advocating for a flexible approach in the application of digital tools.
At the report’s unveiling, Matt Nye, director of the Digital First Programme, NHS England (London), highlighted the pivotal role of digital tools in London’s primary care. Emphasising the potential for digital channels to yield long-term efficiency gains and enhance patient choice, Nye pointed out the benefits of freeing up GP teams’ administrative time to support patients needing alternative access methods.
Amanda Begley, director of digital transformation at HIN South London, reflected on the comprehensive insights gained about the effectiveness of digital primary care. She noted the high adoption rates of the NHS App, online forms, and GP websites, suggesting that minor improvements, as identified in the report, could significantly enhance patient experience and primary care services. Begley also stressed the importance of continually addressing digital exclusion and supporting primary care teams in offering a diverse array of digital and non-digital health management options.
Read More
Can virtual hospitals be the cure for healthcare staffing woes?
The global healthcare sector is currently grappling with a critical shortage of medical professionals. In the United States, the situation has become particularly dire, with over 145,000 healthcare workers leaving their professions by the end of 2022. Experts caution that without addressing the primary concerns of healthcare workers, this shortage is likely to worsen.
Reports by McKinsey and Definitive Healthcare suggest that one potential solution to this crisis lies in the implementation of virtual hospitals, enabling the provision of healthcare services online. This article delves into the key factors contributing to the scarcity of skilled medical staff and examines how virtual patient care can help alleviate these issues.
The Exodus of Healthcare Workers:
The global population is ageing and experiencing deteriorating health, leading to an unprecedented demand for medical services. Even before the recent health crisis, healthcare providers were feeling overwhelmed by this increasing demand, which has only been exacerbated by the COVID pandemic. With a new wave of COVID infections sweeping the US, many medical workers are reluctant to face another surge in hospitalisations. Adding to this is the issue of experienced healthcare professionals nearing retirement age, but opting to leave early due to health concerns. This exodus has left a gap in mentorship and guidance for those still in training.
Governments, regulatory bodies, and healthcare organisations are under pressure to improve medical staff compensation and incentivise people to join the profession. However, some day-to-day challenges faced by healthcare professionals can be mitigated through technological advancements. Clinicians and nurses have expressed a desire for more flexible schedules, the option to work remotely, and increased opportunities for consultation with other experts. Virtual hospitals are a key solution to these needs.
What are Virtual Hospitals?
A virtual hospital is a full-scale digital hospital providing various medical services online and enabling patients to avoid the stress and burden of travelling to a distant brick-and-mortar facility. Virtual hospitals increase healthcare accessibility, helping people with limited access to medical care.
Four Key Benefits of Virtual Hospitals:
Reduced Pressure on Medical Staff:
Virtual hospitals, integrated with remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions, allow medical conditions to be monitored and managed remotely. This integration reduces the necessity for patients to physically visit healthcare facilities, thereby lessening the workload on medical practitioners. Digital communication tools like chat rooms, medical chatbots, and secure video calls enable patients to receive timely medical advice, which can prevent the exacerbation of health issues and decrease unplanned hospital visits.
Increased Job Flexibility:
Virtual hospitals provide healthcare professionals with the flexibility to consult patients and collaborate with colleagues from any location. This flexibility enhances work-life balance and reduces burnout risks. According to FlexJobs’ 2023 Work Insights Survey, 96% of professionals find remote or hybrid work more conducive to mental health. Given that burnout is a leading cause of medical staff shortages, addressing it is key.
Enhanced Intraprofessional Collaboration:
Virtual hospitals facilitate easier collaboration between medical professionals across various locations, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved care quality. This collaboration also aids in faster skill acquisition for new specialists, helping to address gaps in healthcare provision.
Safer Working Conditions:
For healthcare professionals at high risk of contracting infectious diseases like COVID or influenza, virtual interaction with patients and colleagues offers a safer alternative. Additionally, the digital recording of all interactions in virtual hospitals provides a safeguard against workplace harassment and abuse, further ensuring the safety of healthcare workers.
Conclusion:
The healthcare industry is at a pivotal moment where transformation is necessary to meet the growing patient demand. Healthcare workers need improved working conditions, fair compensation, and recognition. While virtual hospitals may not completely resolve the staffing crisis, they play a significant role in enhancing job satisfaction for healthcare professionals. By offering a safer work environment, promoting peer collaboration, and enabling better work-life balance, virtual hospitals can help retain healthcare professionals in the field, thereby ensuring continued provision of high-quality patient care.
Read More
Eli Lilly launches digital health platform LillyDirect for obesity, migraine, and diabetes care
Eli Lilly and Company, a renowned pharmaceutical entity, has unveiled LillyDirect, an advanced digital healthcare platform primarily designed to aid patients in the United States with obesity, migraine, and diabetes management. The official announcement, made on January 4, 2024, marks a significant stride in the field of digital healthcare.
LillyDirect emerges as a multifaceted tool, offering comprehensive services that encompass disease management, support mechanisms, and a streamlined process for medication delivery. A key component of LillyDirect is the LillyDirect Pharmacy Solutions. This feature strategically links users to an external online pharmacy service, simplifying the process of obtaining prescribed medications. This innovation aims to enhance consistency in medication adherence, thereby improving patient health outcomes.
David A. Ricks, the Chairman and CEO of Lilly, expressed the company’s intent behind this launch, emphasising the simplification of the patient experience in a complex healthcare landscape. The underlying goal of LillyDirect is to alleviate patient burdens associated with chronic disease management, ultimately leading to improved health results. LillyDirect presents a novel approach to healthcare access, including a convenient option for home delivery of prescribed Lilly medications, thereby bridging the gap between patients and essential medical resources.
LillyDirect goes beyond just medication provision. It serves as a valuable resource for patients, offering access to a wealth of information and educational materials pertinent to their health conditions. This aspect of the platform enhances patient understanding and engagement with their healthcare journey.
Furthermore, LillyDirect expands the scope of patient support by integrating telehealth services. These digital consultations complement the care provided by patients’ primary healthcare teams. Additionally, the platform facilitates the search for in-person healthcare providers, thereby ensuring comprehensive care management.
Frank Cunningham, Lilly’s Group Vice President of Global Value and Access, highlighted the growing reliance on digital solutions in various aspects of daily life, including healthcare. LillyDirect is envisioned as an innovative solution that caters to the evolving needs of patients, offering an integrated experience in managing health and accessing medications. This initiative reflects Lilly’s commitment to enhancing the quality of life for patients, enabling them to focus on their personal and professional pursuits.
Read More
Singapore forges ahead with digital health initiatives to address healthcare workforce shortages
In Singapore, healthcare leaders and young professionals are uniting under a common goal: to create a more integrated and sustainable healthcare system, leveraging digital technologies. This ambition aligns with findings from the Future Health Index 2023 report by Royal Philips, highlighting Singapore’s dedicated efforts in digital health transformation. These findings reflect broader trends observed across the Asia-Pacific region.
A critical driving force behind this digital push is the projected need for an additional 24,000 allied health professionals and support care staff by 2030, as forecasted by Singapore’s Ministry of Health. This need arises from the growing demands of the nation’s ageing population.
A survey involving 200 senior healthcare executives and young clinicians in Singapore revealed that 75% are either already utilising or planning to adopt digital health technology. This strategic move aims to mitigate the impact of the looming workforce shortage in healthcare. Technologies such as cloud-based solutions, out-of-hospital care innovations, and workflow technologies like digital health records and patient flow automation are at the forefront of this digital transition.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is recognised as a key area of opportunity, with a quarter of respondents currently investing in AI technologies. Over the next three years, a significant 84% have pledged investment in health AI, particularly favouring applications in outcome prediction and clinical decision support.
For young healthcare professionals, the prospect of working in an AI-enabled institution is highly attractive. Furthermore, about half of the healthcare leaders surveyed are investing in virtual care, acknowledged for its substantial role in enhancing patient care.
Singaporean healthcare leaders are also adapting to technology-driven distributed models of care, with about two-thirds of respondents considering themselves well-prepared to work effectively within these new frameworks. These models are anticipated to bring improved work-life balance and job satisfaction for healthcare professionals. They are expected to boost patient compliance with treatment, create additional revenue opportunities, and enhance efficiency and convenience for patients.
In the broader context, Singapore’s commitment to integrating AI in healthcare is further evidenced by the recent memorandum of understanding between Synapxe, its national health technology agency, and Microsoft. This collaboration aims to use generative AI to increase clinical productivity, among other initiatives to modernise public healthcare IT in the country.
Additionally, the Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Singapore’s leading research and development agency, has launched a joint AI lab with health tech company EVYD Technology. This lab is designed to foster multi-institutional and cross-border collaborations in digital health, underpinning Singapore’s robust approach towards embracing digital solutions in healthcare.
Read More
AstraZeneca launches Evinova, aiming to revolutionise clinical trials with digital solutions
AstraZeneca has initiated a foray into the burgeoning field of health technology with the introduction of its new subsidiary, Evinova. Officially unveiled this past Monday (20th of November, 2023), Evinova is poised to redefine how clinical trials are conducted for biotechnology entities, pharmaceutical corporations, and Contract Research Organisations (CROs). By integrating digital health solutions, Evinova aims to significantly curtail the duration and financial outlay required in the medicine development process.
With Evinova’s debut, AstraZeneca has announced several key partnerships. CROs Parexel and Fortrea are set to incorporate Evinova’s digital services into their operations. Furthermore, Evinova is working in conjunction with Accenture and Amazon Web Services to bolster the adoption of its digital products globally and enhance the scalability of its digital offerings.
Evinova will concentrate on three primary service domains within the health-tech sector. First, it will provide unified trial solutions that streamline the collection of clinical trial data, incorporating innovative digitally-enabled endpoints. This data acquisition will be supported by connected medical devices and sensors both onsite at clinical trial locations and remotely in patients’ residences. These solutions aim to bolster telehealth practices, enable remote patient monitoring, and facilitate direct-to-patient medicine dispatches.
Secondly, Evinova is channelling state-of-the-art technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to architect optimally structured clinical trials. This involves assessing and quantifying a multitude of trial characteristics, from environmental impact to patient experience implications.
Lastly, the portfolio management services offered by Evinova seek to provide clients with a comprehensive overview of their drug development portfolio across various stages. This is achieved through predictive algorithms that forecast crucial milestones and allow study leaders to identify and rectify deviations from planned trajectories.
Cristina Duran, Evinova’s newly appointed president, expressed confidence that this strategic move will significantly advance the digital health sector. The objective is to meet the digital solution needs of healthcare professionals and regulators across the pharmaceutical landscape, ultimately enhancing patient care.
This development aligns with AstraZeneca’s recognition of the digital health market’s potential, which is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.6% from 2022 to 2032, reaching a valuation in excess of $900 billion by the end of the forecast period. Evinova stands as a testament to AstraZeneca’s adaptive innovation strategy, aiming to navigate and lead in the digital transformation era of healthcare.
Read More
Virtual care integration elevates patient access and efficiency in Canada clinic
Dr. Richard Tytus, a seasoned medical professional from Hamilton, Ontario, has long championed the merits of virtual healthcare. Being at the helm of a family health team, which comprises around 30 healthcare experts and related professionals, he’s been an early adopter of telemedicine, even before it became a mainstream approach during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Discovering the Potential of Telemedicine
Driven by a commitment to cater to patients who faced physical or psychological challenges that hindered their access to healthcare, Dr. Tytus ventured into telemedicine. He recognised that certain patients were hesitant to step out of their homes due to psychological constraints, effectively limiting their medical outreach. While telephone consultations had been integrated into his practice, the introduction of video conferencing reshaped patient interactions, especially for those requiring exposure therapy.
Embracing a Comprehensive Virtual Healthcare Solution
Initially, Dr. Tytus dabbled in standard video conferencing tools to facilitate patient consultations. However, as the scope of virtual care broadened, he ventured deeper into the realm of specialised telehealth platforms. His vision was an interconnected digital space that mirrored a physical clinic: where patients could move seamlessly from reception to consultation, and even specialist evaluation if required.
Challenges he faced in the early stages of implementing telemedicine provided him with invaluable insights. For Dr. Tytus, it wasn’t merely about leveraging technology but ensuring that the essence of personal patient care wasn’t lost in the digital transition.
Choosing the Right Platform
In the vast sea of telemedicine vendors, Dr. Tytus discovered a standout platform, Banty. What distinguished Banty was not just its fortified security but also its endorsement from government entities. This validation, coupled with its successful security tests and compliance with the ISO 27001 certification, cemented its reputation for robust data protection.
Banty’s platform went beyond simple video consultations. It facilitated intra-team communication with great ease, ensured smooth transfers of patients along with their medical notes, and was adaptable to various electronic health record systems, making it highly versatile.
Measurable Improvements
Dr. Tytus emphasised that one of the most significant outcomes of integrating telemedicine has been removing accessibility barriers for patients. With the hybrid model, which merges in-person and virtual consultations, they’ve achieved not only enhanced patient access but also a boost in operational efficiency.
This operational revamp has led to a tangible surge in patient consultations. Each physician in Dr. Tytus’s team now sees an additional 6-8 patients daily. This shift has also reshaped patients’ perceptions of healthcare, offering a blended approach that caters to individual patient needs.
The technology’s intuitive design has also been a boon for healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on patient care without grappling with tech-related challenges.
Key Takeaways for Aspiring Telemedicine Adopters
For those considering a shift to telemedicine, Dr. Tytus emphasises the importance of patient usability. The system should be straightforward, minimising technical barriers. Furthermore, it should integrate seamlessly into the daily operations of healthcare professionals without a complex learning process. And, importantly, a rigid approach won’t work. The solution must be adaptable, reflecting the unique workflows of different clinics.
In conclusion, Dr. Tytus believes that the essence of telemedicine is not just technology, but the harmonious melding of technology with personalised patient care. The focus should always remain on simplifying and enhancing the healthcare experience for both patients and providers.
Read MoreDigital tool for specialist weight management services shows promising results
In a groundbreaking investigation led by the team at University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust (UHCW), the potential and efficacy of digital platforms tailored for advanced weight management have been highlighted.
The research revolved around assessing the eagerness, acceptance, and active participation of patients on standby for their first-ever specialist weight management consultation. In the United Kingdom, specialised weight management services, often referred to as tier 3 services, offer a holistic approach to tackling obesity. These specialised services are generally anchored in hospitals or clinic facilities and bring together a diverse group of healthcare specialists. This includes dietitians, psychologists, specialist nurses, and doctors, all proficient in the realm of weight management.
For the purposes of this research, an NHS-approved digital platform named Gro Health was integrated into the service offering. This avant-garde health application propels numerous healthcare routes, with its tier 3 weight management feature, “W8Buddy”, acting as an online weight loss clinic. This feature delivers structured learning sessions, both individual and group coaching, an expansive list of over 2,000 recipes and meal schedules, and tools for health and nutrition tracking to chart progress.
The study drew in 199 prospective patients eagerly waiting for their appointment at the NHS Trust’s tier 3 weight management service.
Preliminary results indicate that over half of these individuals expressed genuine interest in the application. An impressive one-third went on to actively engage with the digital platform, highlighting the immense potential of such digital interventions in the specialised weight management scenario.
The engagement analysis unearthed intriguing data points. Those prone to emotional eating or those with an escalated BMI exhibited an increased propensity towards the Gro Health application. Meanwhile, aspects like age, ethnic background, and metabolic indicators like glycemia and lipid readings did not notably sway the interest.
These findings could serve as a blueprint for revolutionising weight management strategy. As digital healthcare tools evolve and gain traction, they stand poised as formidable and expansive strategies to confront the global issue of obesity.
Charlotte Summers, a behavioural change expert and the Founding Chief Operations Officer, expressed her enthusiasm, noting, “The pronounced interest demonstrated by patients in the Gro Health W8Buddy tool for weight management is truly heartening.”
She drew attention to the evident link between emotional eating, a raised BMI, and heightened engagement, highlighting, “This relationship underscores the transformative capacity of precise digital strategies in addressing weight-related concerns.”
Summers further elaborated on the journey ahead, “As we venture into providing tier 3 and 4 weight management services, we’re thrilled about tailoring these platforms with firsthand insights from both patients and healthcare providers. Such a collaborative effort not only champions a patient-driven model but also deepens our grasp on their preferences and anticipations. This, in turn, empowers us to offer top-tier, accurate care, be it through enhancing conventional healthcare avenues or pioneering virtual healthcare experiences.”
The study’s authors stress the need for continued exploration into understanding the challenges and motivators behind adopting digital tools and emphasise the importance of rigorously assessing their impact within specialised weight management services.
The rise of digital health platforms is sculpting the future of healthcare. This specific investigation underscores the transformative power of such tools, all while highlighting the necessity to unravel the complexities of patient engagement. As we witness the proliferation and capabilities of digital health platforms, the persistent quest to maximise their utility for patients and the broader healthcare spectrum is paramount.
Stay tuned for more revelations as ongoing studies continue to sculpt this rapidly evolving domain of weight management.
Read More
WHO Europe stresses the need for strengthened digital health literacy across the region
In a significant report released by WHO Europe, there’s an emphasised call for an immediate boost in investments towards digital health literacy across the region.
The report, titled “Digital Health in the European Region: The Ongoing Commitment to Transformation,” sheds light on a concerning statistic: only half of the countries spanning Europe and Central Asia have rolled out policies tailored to bolster digital health literacy. This oversight leaves a considerable portion of the population in the shadows, devoid of the benefits of evolving digital healthcare platforms.
The landscape of healthcare has experienced a monumental shift in the WHO European Region over recent times, as is evident from the burgeoning adoption rate of digital health solutions. This transformation has redefined the dynamics of patient care.
Released during the Second WHO Symposium on the Future of Health Systems in a Digital Era held for the European Region, the report encompasses insights from all 53 member nations. Many countries within this bracket witnessed a spontaneous surge in the creation and deployment of digital health tools and policies due to the pressing demands of the COVID-19 pandemic – a time dominated by lockdowns and social distancing mandates. This led to the broader acceptance of telemedicine services and the advent of user-centric health applications. However, the report firmly stresses that the journey is far from complete.
A pressing concern is the evident disparity in the adoption and assimilation of digital health solutions across the region. This “digital health divide” implies that a staggering number of individuals are yet to harness the potential benefits of digital health advancements.
Diving deeper, the report draws attention to several pivotal areas:
- Of the countries surveyed, 44 have an established national digital health strategy.
- A unanimous consensus is seen with all 53 member nations having legislation that focuses on protecting individual data privacy.
- However, there’s a considerable disparity in the preparedness and execution, with only 19 countries offering guidance on evaluating the efficacy and safety of digital health initiatives.
- Slightly above 50% of these countries have put forth policies advocating digital health literacy and have set into motion a digital inclusion agenda.
- The pandemic saw 30 countries devising legislation to champion the cause of telehealth.
- An area that requires immediate attention is the oversight of mobile health (mHealth) applications. Many nations lack a dedicated body to ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of these apps. A mere 15% have reported systematic evaluations of state-backed mHealth initiatives.
- Just above half of the countries have strategised the application of Big Data and avant-garde analytics within the healthcare domain.
Dr. Hans Henri P. Kluge, the WHO Regional Director for Europe, opined on the matter, “In numerous nations, the growth trajectory of digital health platforms has been somewhat sporadic. This approach warrants an overhaul. It’s imperative to perceive digital health as a long-term, strategic investment, rather than a fleeting addition or a privilege enjoyed by a select few. It is a clarion call for our political and health leaders to strategically invest in the digital health infrastructure of tomorrow, today.”
Read More